Billing Provider
Introduction
In healthcare, medical billing serves as a crucial process that ensures the financial health of medical practices and facilitates smooth transactions between patients, healthcare providers, and insurance companies. One key component in this process is the role of the "Billing Provider." This term, previously often referred to by the "Tax ID" in medical billing systems, has evolved to emphasize the provider's pivotal role in the billing and payment cycle.
What is a Billing Provider?
A billing provider refers to the entity or individual responsible for receiving payments from payers, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance companies, for medical services rendered. This can be a healthcare practitioner, a group practice, or a hospital. The billing provider is typically the legal entity that owns the medical practice or the individual under whose name the practice is credentialed with insurance payers.
Understanding the Implementation of Billing Providers on Professional (1500) and Institutional Claims (UB04, 1450)
Medical billing in the United States typically involves two primary types of claim forms: the CMS-1500 and the UB-04. Each form caters to different types of healthcare providers and services. Here's how the "Billing Provider" is implemented in these forms:
Professional Claims (CMS-1500)
For professional claims, the CMS-1500 form is utilized. This form is designed for healthcare providers who bill for professional services, including physicians, nurse practitioners, and physical therapists. The billing provider's information on the CMS-1500 includes:
- Box 33: This box is designated for the billing provider’s name, address, and phone number. It’s essential for ensuring that payments and correspondence from the payer are directed to the correct location.
- Box 33a: This includes the National Provider Identifier (NPI) of the billing provider. The NPI is a unique identification number for covered health care providers.
The information must accurately represent the legal entity or individual entitled to receive payment for the services rendered.
Institutional Claims (UB-04, CMS-1450)
The UB-04 form, also known as CMS-1450, is primarily used by hospitals, nursing facilities, and other institutional providers. The implementation of the billing provider on the UB-04 includes:
- Field 1: This field is for the name and address of the billing provider. It’s the primary identifier on the claim for where services were provided and who is billing for these services.
- Field 56: This is where the NPI of the billing provider is entered.
- Field 57: This field is for other identifiers, like the TIN or EIN
Managing the Billing Provider List: Where to go?
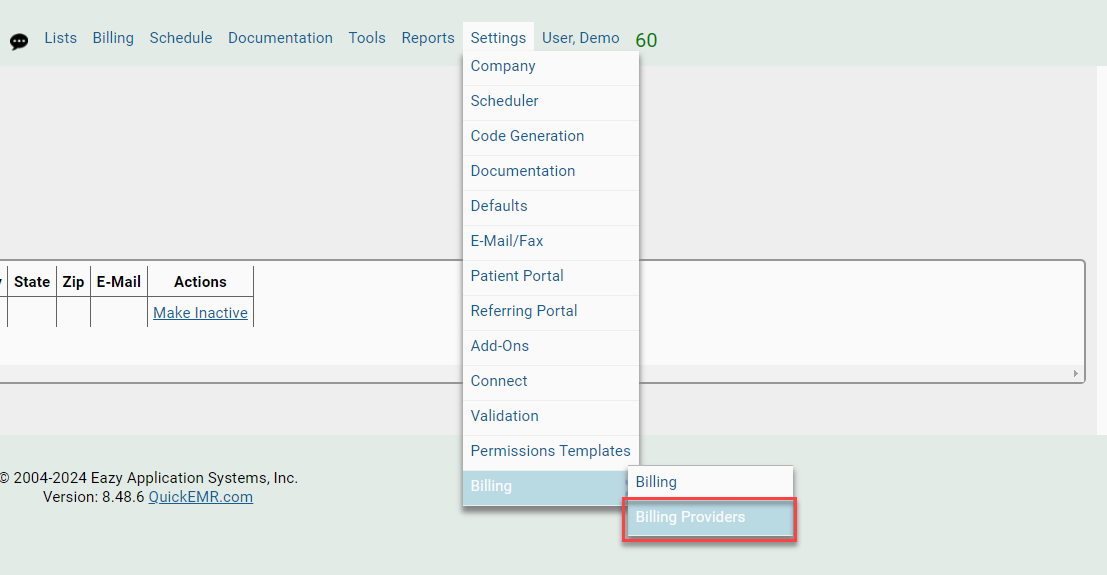
Mapping from QuickEMR to EZclaim
Related Articles
QEMR Native (Self Pay Billing Management System)
**This system is for facilities that ONLY accept cash-pay patients and is not yet intended for facilities that are submitting claims to insurances** Enabling QuickEMR Native: Where to go? 1. The Quickemr Native system can be enabled by going under ...QuickEMR Note Validation
Note Validation Permission to Complete To allow a user to complete a note, the user must be given permission in the user settings. 1. Navigate to Lists --> Users 2. Select the user, followed by selecting the Settings tab on the left side of the ...How to set up credit card payment system within QuickEMR?
How to get started: The first step to setting up the credit card payment system is to contact Gravity Payments. You will need to create an account with Gravity, who will then send over your account information to QuickEMR so we can properly set up ...Benefit & Eligibility Checking
QuickEMR now supports benefits & eligibility lookup for over 800 payers. This article describes the setup and usage of this new feature. Terms and Conditions for Use Warning! This feature will incur additional charges per transaction. By using this ...HL7 SFTP Export
A generic HL7 interface using HL7 ~2.3.1 ADT messages are sent upon creating or updating as case. DFT messages are sent through Batch Management. ZPM messages are sent when a payment is flagged to "Export". The ZPM is a custom packet type but uses ...